z factor for pipette calibration|how to adjust pipette calibration : solutions Z-factors-calibration_2017_01_26.docx 1/1 26. January 2017. Table 1: Z-correction factors for distilled water as a function of test temperature and air pressure. How to use the z-correction . The autoclave is a sealed device (similar to a pressure cooker) that kills microorganisms using saturated steam under pressure.
{plog:ftitle_list}
What do I do if I get a failed (positive) Biological Indicator? Just like a smoke detector alarming, a failed biological indicator tells sterile processing staff that action needs to .
pipette calibration z factor chart
Check if your pipette needs to be calibrated: Learn how to calculate pipette accuracy and precision to compare the values obtained with the specifications.
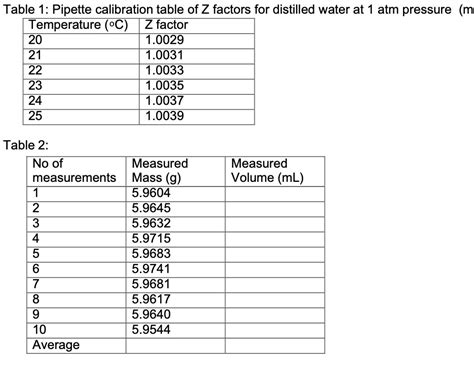
Z-factors-calibration_2017_01_26.docx 1/1 26. January 2017. Table 1: Z-correction factors for distilled water as a function of test temperature and air pressure. How to use the z-correction .Z factor (Z correction factor). The volumetric value can be obtained by multiplying the measured mass value with the Z factor. . From what has been discussed above, uncertainty in volume calibration using A&D’s pipette accuracy testers can be calculated as follows: 1) AD-4212B-PT (Measurement of 20 μL) Category Item Standard uncertainty of Calibration by using different set volumes of 10 µl, 50 µl and 100 µl for 100 µl pipette (Refer Table-2) Calibration by using different set volumes of 500 µl, 2500 µl and 5000 µl for 5000 µl pipette (Refer Table-3) . Conversion factor (Z) = 1.0040 µl/mg; The percent variation can be calculate as formula given below % Variation =(100 .
yellow gilson pipette tips
pipette calibration protocol
The Z factor is not only depending on the density of water adjusted to th e local temperature and pressure . Pipettes calibration by the gravimetric method is t he best suited for measuring the .
in Standard Methods of Pipette Calibration George Rodrigues, Ph.D. Senior Scientific Manager ARTEL [email protected] June, 2003 . This weight is converted to volume using the “Z factor,” which properly accounts for the air buoyancy and liquid density effects. The Z factor is a function of the temperature of the water .This paper discusses the calibration of pipette, with particular attention to the type that is used and calibrated most frequently. This is the so-called air-displacement pipette, single channel, adjustable volume pipet. . This correction factor is called the Z-factor as defined in ISO 8655-6 [2]. Method and Points of AttentionNote: On INTEGRA's electronic pipettes you can set a calibration reminder either in days or cycles. 1. Environment and materials Environment. Draft free, constant temperature between 15 °C and 30 °C, max. ±0.5 °C deviation during the measurements. . Z = Z factor. Here is an example of how to convert balance readings for a 100 µl single .to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of water. Then the calculated volume of water is compared with the theoretical volume to determine the accuracy and precision of the pipette. 2. Material and equipment: (1) pipette and tips (2) 50 ml beaker and plastic medicine cup (3) distilled water ( >=10MQ ) (4) temperature meter ( ±0.1℃ )
The air pressure decreases at higher altitudes and the conversion factor Z decreases as well. The boiling point of some liquids can also change to quite close to room temperature, increasing the evaporation loss dramatically. . Calibration of Pipettes. Calibration of Pipettes, officially means determining the difference between the dispensed .
to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of water. Then the calculated volume of water is compared with the theoretical volume to determine the accuracy and precision of the pipette. 2. Material and equipment: (1) pipette and tips (2) 50 ml beaker and plastic medicine cup (3) distilled water ( >=10MQ ) (4) temperature meter ( ±0.1℃ )A new 5-place analytical balance with a pipette calibration kit (Fig.1) and an Artel PCS®3 Pipette Calibration System (Fig. 2) were studied to determine their performance capabilities in calibrating pipettes. Several tests were conducted to evaluate the sources of uncertainty associated with both pipette calibration systems and the The calibration of pipette is carried out by gravimetric method. When determining the volume of water, the accuracy of measurements is effected by ambient temperature, atmospheric pressure and relative humidity. These factors are usually combined to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of water.
C. Calibration and Adjus tment Pipettes are factory calibrated and adjusted to give the volumes as specified with . The factor Z is for converting the weight of the water to volume at test temperature and pressure. A typical value is .0032 µl/mg at 22°C and 95 kPa.Easily calibrate pipettes, perform interim verifications, standardize operator skills and manage inventory. Fast, accurate, and precise, the PCS is a portable and easy-to-use volume verification system that simplifies single-channel pipette calibration, interim volume verification, and pipette user/operator training and competency assessment.The Z factor is not just equal to the density of liquid adjusted to the local temperature and pressure. It also takes into account the air density and density of weights used to calibrate the . balance calibration [7]. 3. Typical Examples of Z factor Calculation Values of the conversion factor Z (µL/mg) as a function of temperature and .
yellow pipette tip
For the calibration or adjustment of pipettes, the scales and measuring station should fulfill the following requirements: 1.1 Balances 1.1.1 Balance type Use semi-microbalances and microbalances to calibrate pipettes. Some companies offer balances that are specially designed to meet the requirements of pipette calibration, e.g. Sartorius and .
17 Quarterly Pipette Calibration (gravimetric) Date Analyst Balance Ae 240 Temp. (C) Z-Factor #N/A Serial # J52053 Pipette # Pipette # Pipette # VOLUME WEIGHT VOLUME WEIGHT VOLUME WEIGHT
Gilson’s Specifications for Pipette Calibration are Stricter than ISO 8655 Guidelines. Gilson’s requirements are more stringent than the maximum tolerated errors defined by ISO 8655-2 as we feel this is important for those using pipettes for research, diagnostics, and QC. Below are two examples of Gilson’s stringent requirements for .
in Standard Methods of Pipette Calibration George Rodrigues, Ph.D. Senior Scientific Manager ARTEL . The Z factor is a function of the temperature of the water (TW), .An experienced and properly trained technologist is required to accurately perform calibration of MLA Pipettes, using the gravimetric method. All procedures are to be performed under controlled environmental conditions (see Section III). . • Z factor (see Table 2, Appendix A) (The Z factor is required in the volumetric calculations to .A pipette is only as good as the user and the calibration checks that are carried out routinely to check for accuracy and precision. You will receive your new pipette with a calibration certificate, but this will need to be verified for continual use and the pipette kept in tip top condition if results are to be meaningful.Pipette Calibration Table of Z-Factors From: Pipette Performance Check. Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene, ESS INO GENOP 200, Revision 1, January, 2001. Temperature (°C) Z-Factor 15 1.0019 15.5 1.0020 16 1.0021 16.5 1.0022 17 1.0023 17.5 1.0024 18 1.0025 18.5 1.0026 19 1.0027 19.5 1.0028 20 1.0029 20.5 1.0030 21 1.0031 21.5 1.0032
Pipette Calibration. A pipette is a laboratory device used in chemistry, biology and medicine to dispense a measured volume of liquid from one container to another. Regular calibration and servicing are essential and, in addition, pipettes also require frequent checking for .What is the Z factor in pipette calibration? The calibration of pipette is carried out by gravimetric method. When determining the volume of water, the accuracy of measurements is effected by ambient temperature, atmospheric pressure and relative humidity. These factors are usually combined to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of .
METTLER TOLEDO optimizes your pipette calibration process – meeting requirements. Reliable scheduling The task list gives a concise overview of all pipettes to be calibrated. . Advanced options of customization, e.g. calculation of the Z factor thanks to an equation editor • • • .Note: On INTEGRA's electronic pipettes you can set a calibration reminder either in days or cycles. 1. Environment and materials Environment. Draft free, constant temperature between 15 °C and 30 °C, max. ±0.5 °C deviation during the measurements. . Z = Z factor. Here is an example of how to convert balance readings for a 100 µl single . Note: On INTEGRA's electronic pipettes you can set a calibration reminder either in days or cycles. 2 Environment and materials 2.1 Environment. Draft free, constant temperature between 15 °C and 30 °C, max. ±0.5 °C deviation during the measurements. . Z = Z factor ; Calculate the mean volume per test volume and per channel: V = mean .
1. Classification for calibration of volumetric apparatus Table 1 S. No. Description Relevant standard Permanen t facility Onsite calibration Mobile facility 1. Burettes (manufactured as per ISO 385) ISO 4787:201 0 Yes No Yes * 2. Single-volume (one mark) pipettes (manufactured as per ISO 648) ISO 4787:201 0 Yes No Yes * 3. Graduated pipettes
pipette calibration chart

Contamos con un extenso portafolio de autoclaves de laboratorio para cubrir múltiples aplicaciones y segmentos del mercado. Descubre la combinación de modelo de autoclave y accesorios que mejor se adapta a tus necesidades .
z factor for pipette calibration|how to adjust pipette calibration